数据结构之队列
1.简介
队列是一种特殊的线性表,特殊之处在于它只允许在表的前端(front)进行删除操作,而在表的后端(rear)进行插入操作。
队列和栈一样,是一种操作受限制的线性表。进行插入操作的端称为队尾,进行删除操作的端称为队头。故队列又称为先进先出(FIFO—first in first out)线性表。
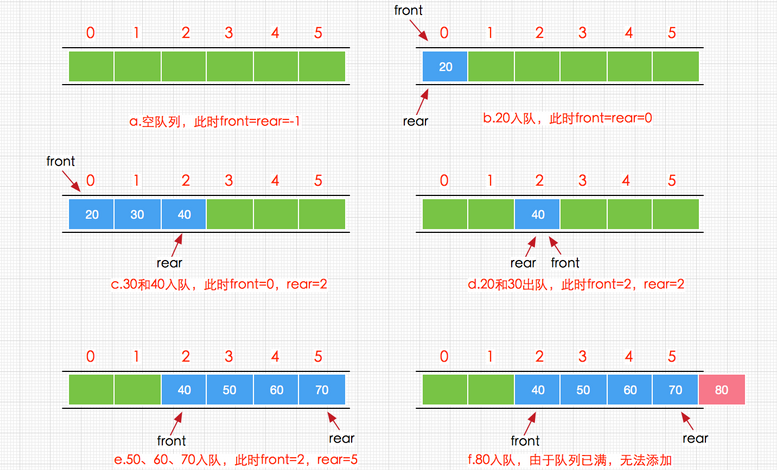
队列包含的基本操作:
1.入队操作:在队尾插入数据
2.出队操作:在对头删除数据
3.队列中没有元素时,称为空队列
4.队列中存储达到预定上限,称为队满
队列可以使用数组或链表作为物理存储结构,使用数组实现的队列称为顺序队列,使用链表实现的队列称为链式队列。
2.顺序队列
顺序队列使用数组作为物理存储结构,数组特点是内存连续,并且在初始状态就定义了数组的大小。数组在出队时后,需要注意对数据进行搬移。
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct SeqQueue {
int* buf; // 队列中存储空间的指针
int head; // 队头
int tail; // 队尾
int maxSize; // 队列最大值
};
// 初始化队列
void init(struct SeqQueue* que, int size)
{
que->head = 0;
que->tail = 0;
que->buf = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * size);
que->maxSize = size;
memset(que->buf, 0, sizeof(int) * size);
}
// 队列释放
void destroy( struct SeqQueue* que )
{
free(que->buf);
que->buf = NULL;
}
// 遍历队列数据
void display(struct SeqQueue* que)
{
printf("queue size = %d, show queue: ", que->tail - que->head );
int i = 0;
for (i = que->head; i != que->tail; i++) {
printf("%d,", que->buf[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// 队列是否为满
int isfull(struct SeqQueue* que)
{
return (que->tail - que->head) == que->maxSize;
}
// 队列是否为空
int isempty(struct SeqQueue* que)
{
return que->tail == que->head;
}
// 入队
int push(struct SeqQueue* que, int val)
{
if ( isfull(que)) { // 队满,无法插入
return -1;
}
if (que->tail == que->maxSize) { // 如果队尾已经到了边界,需要把队列数据向数组最开始进行数据搬移
memmove(que->buf, que->buf + que->head, (que->tail - que->head)*4 );
que->tail -= que->head;
que->head = 0;
}
que->buf[que->tail] = val;
que->tail++;
return que->tail - 1; // 返回插入位置,该位置可能进过数据搬移
}
// 出队
int pop(struct SeqQueue* que)
{
if (isempty(que)) {
return -1;
}
return que->head++;
}
int main()
{
struct SeqQueue queue;
init(&queue, 5);
display(&queue);
push(&queue, 20);
push(&queue, 30);
push(&queue, 40);
push(&queue, 50);
push(&queue, 60);
display(&queue);
printf("push = %d\n", push(&queue, 70) ); // 队满,此时无法插入
display(&queue);
printf("pop = %d\n", pop(&queue) );
printf("pop = %d\n", pop(&queue) );
printf("push = %d\n", push(&queue, 70)); // 经过搬移,可以插入数据
display(&queue);
destroy(&queue);
return 0;
}
3.链式队列
链式队列是基于链表实现的顺序表,区别于顺序队列它的内存可以是不连续的,队头和队尾的操作无需进行数据搬移。
struct LinkNode {
struct LinkNode* next;
int val;
};
struct LinkQueue {
struct LinkNode head; // 始终作为头节点
struct LinkNode* tail; // 始终指向队列最后一个节点
};
void init(struct LinkQueue* que)
{
que->head.next = NULL;
que->tail = &que->head;
}
void display(struct LinkQueue* que)
{
if (que->head.next == NULL) { // 队列无节点
return;
}
printf("show queue: ");
struct LinkNode* ptr = que->head.next;
while (ptr != que->tail) {
printf("%d, ", ptr->val);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void push(struct LinkQueue* que, int val)
{
struct LinkNode* node = (struct LinkNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct LinkNode));
node->val = val;
node->next = NULL;
que->tail->next = node;
que->tail = node; // 队尾指针始终指向最后一个节点
}
struct LinkNode* pop(struct LinkQueue* que)
{
struct LinkNode* ret = NULL;
ret = que->head.next;
if (ret == NULL) {
return NULL; // 队列空,返回空
}
que->head.next = ret->next; // 返回头结点地址
return ret;
}
int main()
{
struct LinkQueue queue;
init( &queue );
display(&queue);
push(&queue, 20);
push(&queue, 30);
push(&queue, 40);
push(&queue, 50);
push(&queue, 60);
display(&queue);
push(&queue, 70);
display(&queue);
printf("pop = %p\n", pop(&queue) );
printf("pop = %p\n", pop(&queue) );
push(&queue, 70);
display(&queue);
return 0;
}



